In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing, finding the perfect balance between multiple advertising channels can be a daunting task. With the rise of multi-channel advertising campaigns, understanding how to effectively handle attribution modeling becomes crucial. But fear not, as this article aims to shed light on this complex issue and provide you with practical insights and strategies to navigate through the challenges of attribution modeling. So, let’s dive right in and discover the secrets behind optimizing your multi-channel advertising campaigns!
Understanding Attribution Modeling
Definition of Attribution Modeling
Attribution modeling, in the context of multi-channel advertising campaigns, refers to the process of assigning credit to different marketing touchpoints for driving conversions or desired actions. It helps advertisers understand which channels or tactics are most effective in their customer journey and allocate resources accordingly.
Importance of Attribution Modeling in Multi-channel Advertising Campaigns
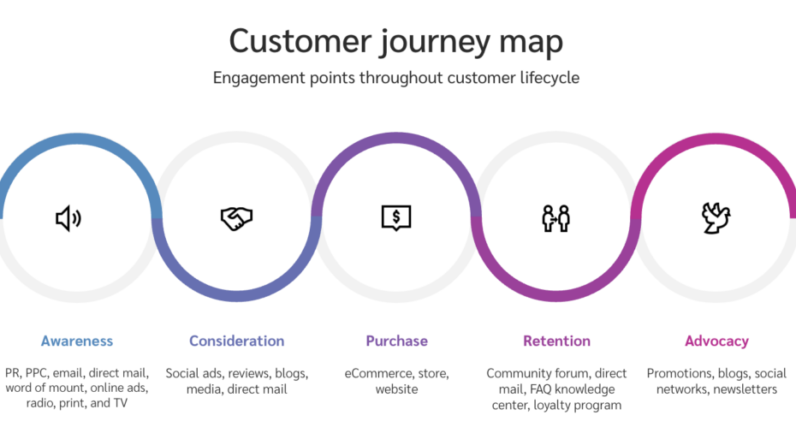
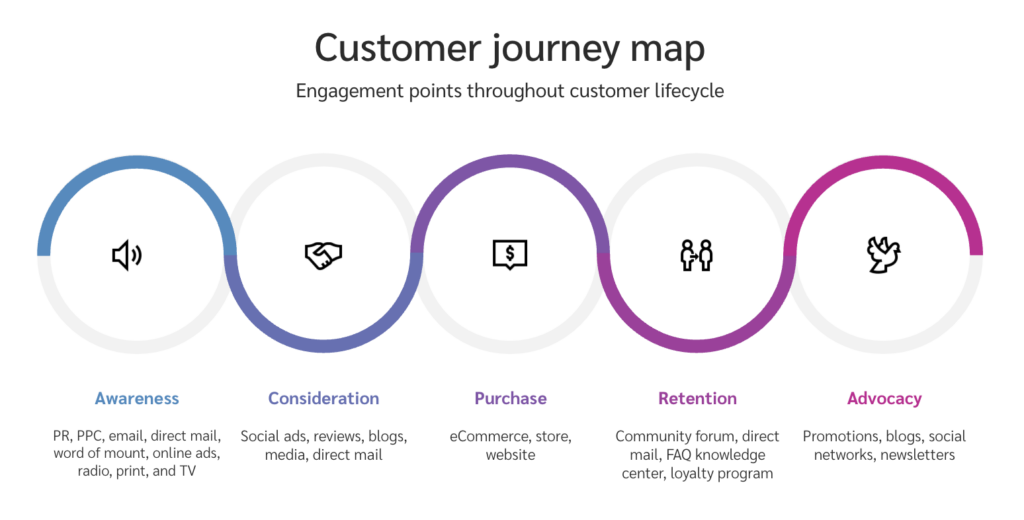
In today’s digital landscape, consumers interact with brands through various touchpoints, such as websites, social media, emails, and ads. Attribution modeling allows advertisers to measure the impact of each touchpoint on the customer’s decision-making process. Without proper attribution, it can be challenging to accurately gauge the effectiveness of different marketing channels and make informed decisions about budget allocation.
Types of Attribution Models
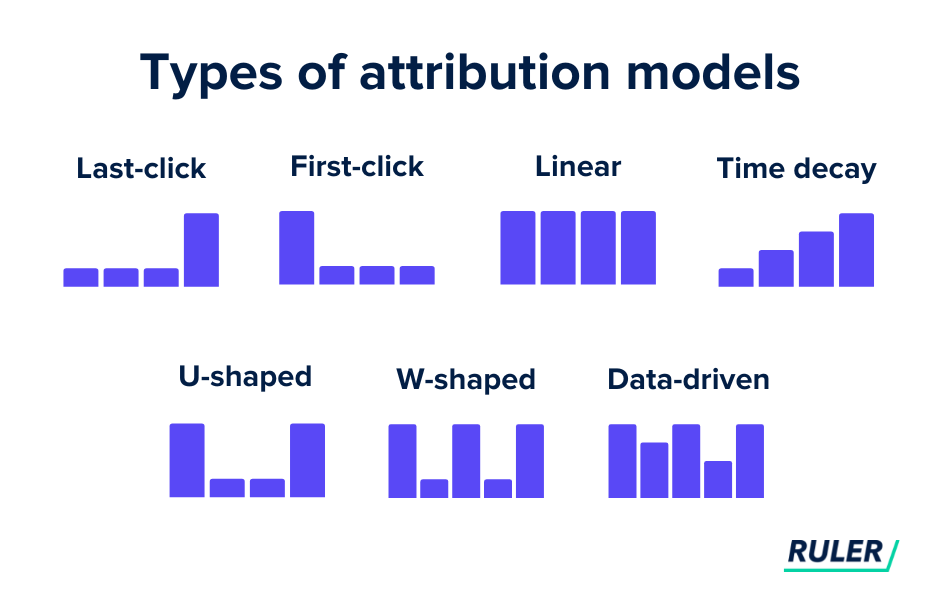
There are several attribution models available, each with its own approach to crediting conversions. Some common attribution models include:
-
First-Touch Attribution Model: This model assigns full credit for a conversion to the first touchpoint that a customer interacts with. It is useful for understanding the initial engagement that leads to conversion.
-
Last-Touch Attribution Model: In contrast to the first-touch model, the last-touch attribution model gives all credit for a conversion to the last marketing touchpoint before the conversion occurs. It highlights the final action that influenced the customer’s decision.
-
Linear Attribution Model: The linear attribution model distributes equal credit to each touchpoint throughout the customer journey. It provides a more balanced view of the impact of all marketing efforts.
-
Time Decay Attribution Model: This model gives more credit to touchpoints closer to the conversion and less credit to earlier touchpoints. It acknowledges the diminishing influence of initial engagement as the customer gets closer to making a decision.
-
Position-Based Attribution Model: Also known as the U-shaped model, this attribution model gives significant credit to the first and last touchpoints, and distributes the remaining credit among the intermediate touchpoints. It recognizes the importance of both the initial and final interactions.
-
Custom Attribution Models: Advertisers can also create customized attribution models tailored to their specific business needs and objectives. These models can consider various factors, such as engagement duration, click-through rates, or specific events.
Choosing the Right Attribution Model for Your Campaign
Selecting the most suitable attribution model depends on your campaign objectives, the nature of your business, and the complexity of your customer journey. Each model has its strengths and limitations, so it’s crucial to consider factors such as the length of the sales cycle, the number of touchpoints involved, and the importance of different stages in the conversion process. Experimentation and testing different models can help determine the most effective one for your business.
Setting Up Multi-channel Advertising Campaigns
Defining Campaign Objectives
Before setting up a multi-channel advertising campaign, it’s essential to define clear objectives. Understanding what you want to achieve through your campaign will help guide your strategy and determine the metrics you need to track. Whether it’s driving website traffic, generating leads, increasing sales, or improving brand awareness, clearly defining your goals will ensure your efforts align with your overall marketing objectives.
Choosing Appropriate Advertising Channels
Once you have defined your campaign objectives, the next step is to select the most appropriate advertising channels. Consider factors such as your target audience, their preferences, and the nature of your products or services. For example, if your target audience is predominantly active on social media, allocating a significant portion of your budget to platforms like Facebook and Instagram might be more effective than traditional media channels. Thorough research and understanding of your target market will help ensure you choose the right mix of channels for your multi-channel campaign.
Allocating Budgets among Channels
Budget allocation among different channels is a critical aspect of multi-channel advertising campaigns. Based on your campaign objectives, you need to distribute your budget in a way that optimizes your reach and maximizes your return on investment (ROI). Consider factors such as the cost per acquisition (CPA) for each channel, the historical performance of your campaigns, and the estimated reach and engagement potential of each channel. It’s often beneficial to allocate a portion of your budget for testing and experimentation to find the most effective channel mix.
Implementing Tracking and Analytics
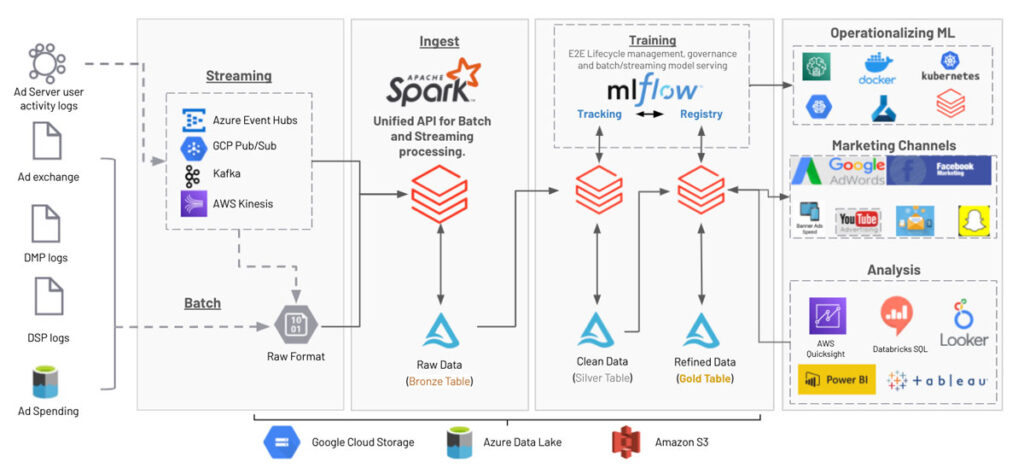
To effectively measure the performance of your multi-channel advertising campaigns, it’s crucial to implement tracking and analytics systems. Tracking mechanisms, such as pixels, cookies, or unique URLs, enable you to monitor customer interactions across various touchpoints. Analytics tools, such as Google Analytics or Adobe Analytics, help you gather and analyze data to gain insights into the effectiveness of your campaigns. Implementing robust tracking and analytics systems ensures the availability of accurate data to inform your attribution modeling and campaign optimization efforts.
Attribution Models and Their Metrics
First-Touch Attribution Model
The first-touch attribution model attributes full credit to the channel or touchpoint that initiates a customer’s engagement with your brand. In this model, the first touchpoint or marketing tactic that drives a visitor to your website or generates the initial interest receives all the credit for any subsequent conversions or actions. The metrics commonly associated with the first-touch model include the number of website visits, ad impressions, or click-through rates.
Last-Touch Attribution Model
The last-touch attribution model, as the name suggests, gives credit exclusively to the channel or touchpoint that directly leads to a conversion or desired action. Under this model, the last marketing touchpoint that a customer interacts with before completing a purchase or submitting a form receives full credit. Key metrics associated with the last-touch model may include conversion rates, leads generated, or revenue generated.
Linear Attribution Model
The linear attribution model assigns an equal proportion of credit to each touchpoint or marketing channel that contributes to a conversion or action. This approach acknowledges that the customer journey is multifaceted and involves multiple touchpoints, providing a more balanced view of the effectiveness of each marketing effort. Metrics associated with the linear attribution model include equal credit distribution across all touchpoints, engagement rates, or customer interactions.
Time Decay Attribution Model
The time decay attribution model attributes the highest credit to the touchpoints or channels closest to the conversion event. It recognizes that the influence of marketing touchpoints tends to increase as the customer gets closer to making a decision. The time decay model assigns lower credits to earlier touchpoints, reflecting the diminishing impact over time. Conversion metrics tied to the time decay model may include click-through rates, conversion time, or engagement duration.
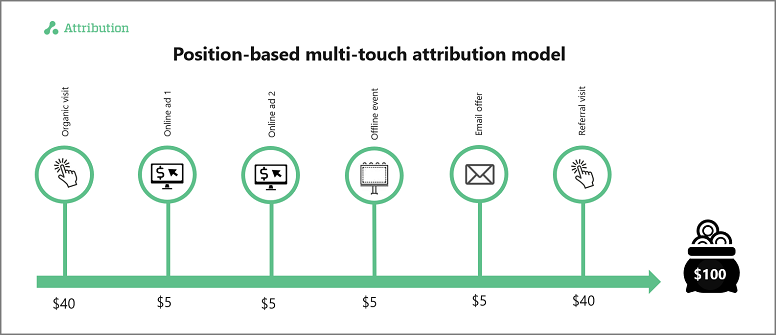
Position-Based Attribution Model
The position-based or U-shaped attribution model offers a balanced approach by assigning significant credit to both the first and last touchpoints, while distributing the remaining credit among the intermediate touchpoints. This model acknowledges the initial and final interactions as crucial in the customer’s decision-making process. Metrics commonly associated with the position-based model include first-touch conversions, last-touch conversions, or engagement rates across all touchpoints.
Custom Attribution Models
Custom attribution models allow you to tailor the attribution process to your specific business needs and customer journey complexity. By defining the parameters and rules that attribute credit to different touchpoints, you can create a model that aligns with your unique business objectives. Custom attribution models often involve considering additional metrics and variables specific to your industry or audience.
Conversion Metrics to Consider
In addition to the various attribution models, it’s important to consider a range of conversion metrics when analyzing the effectiveness of your multi-channel advertising campaigns. Some common conversion metrics include:
-
Conversion Rate: The percentage of visitors who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form.
-
Cost per Acquisition (CPA): The cost incurred to acquire a new customer or generate a conversion.
-
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): The predicted value a customer brings to your business throughout their relationship with your company.
-
Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): The revenue generated as a result of advertising efforts, compared to the cost of those efforts.
-
Attributed Revenue: The revenue specifically assigned to a particular touchpoint or channel based on the attribution model used.
Understanding and analyzing these metrics in conjunction with the chosen attribution model will provide a comprehensive view of campaign performance and help guide optimization efforts.
Implementing Attribution Modeling
Collecting Data from Multiple Channels
To implement attribution modeling, it is crucial to collect data from multiple channels. This involves tracking customer interactions across various touchpoints, including websites, social media platforms, email, paid advertisements, and offline channels if applicable. Implementing mechanisms such as tracking pixels, UTM parameters, or customized tracking links enables data collection and ensures a holistic view of customer behavior.
Consolidating and Cleansing Data
Once data has been collected from multiple channels, it is essential to consolidate and cleanse the data for accurate attribution modeling. This process involves removing duplicate entries, correcting data inconsistencies, and standardizing data formats. By ensuring the data used for attribution modeling is clean and reliable, you can make informed decisions based on accurate insights.
Data Visualization Tools and Platforms
To make sense of the vast amount of data collected, data visualization tools and platforms can be leveraged. These tools enable marketers to transform complex data into visually appealing charts, graphs, and dashboards, making it easier to identify trends, patterns, and key insights quickly. Platforms such as Tableau, Google Data Studio, or Power BI offer robust visualization capabilities that aid in understanding the attribution modeling results.
Attribution Modeling Software and Solutions
Using specialized attribution modeling software and solutions can streamline and automate the attribution process. These tools leverage advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to determine the contribution of various touchpoints and channels more accurately. Examples of attribution modeling software include Google Attribution, Adobe Analytics, or Neustar MarketShare. By utilizing these tools, advertisers can save time and gain more precise insights into campaign performance.
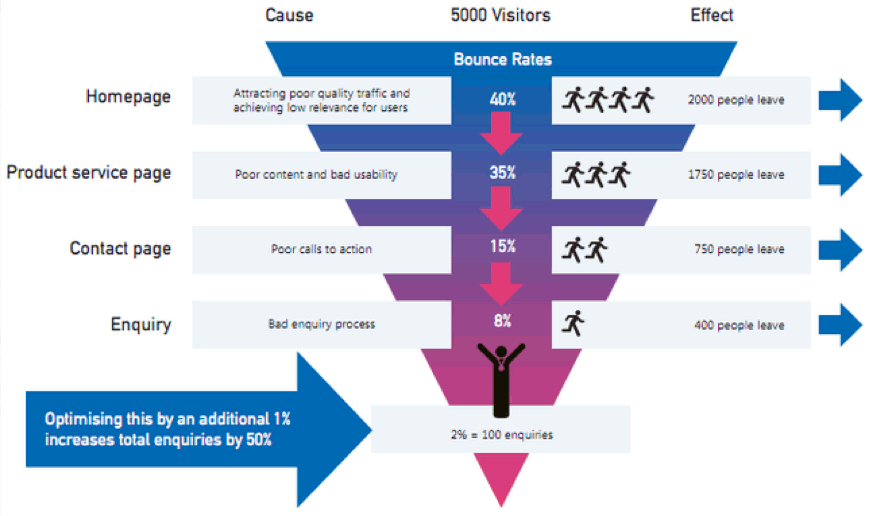
Analyzing Attribution Modeling Results
Reporting and Dashboards
To effectively analyze attribution modeling results, reporting and dashboards play a crucial role. Reporting provides a summary of the attribution model’s performance, including key metrics, conversion rates, and revenue distribution across touchpoints. Dashboards serve as real-time data visualization tools, allowing advertisers to track and monitor campaign performance while gaining insights into the most effective channels and touchpoints.
Interpreting Attribution Results
Interpreting attribution results involves understanding the proportion of credit assigned to each touchpoint or channel based on the selected attribution model. Advertisers can assess the impact of their marketing efforts at different stages of the customer journey and identify the touchpoints that contribute most significantly to conversions. This analysis helps prioritize and optimize marketing investments to improve campaign performance.
Identifying Key Insights and Trends
The analysis of attribution modeling results often reveals valuable insights and trends. By identifying patterns in customer behavior, marketers can understand which touchpoints or channels are most influential in driving conversions. This knowledge can guide strategic decision-making and enable marketers to tailor their marketing efforts to the preferences and behaviors of their target audience.
Optimizing Campaign Performance
One of the primary benefits of attribution modeling is its ability to optimize campaign performance. By analyzing attribution results, marketers can identify underperforming touchpoints or channels and reallocate resources to those that generate more significant impact. Continuous optimization and experimentation based on attribution modeling insights can lead to improved ROI and overall campaign effectiveness.
Challenges and Limitations of Attribution Modeling
Data Integration and Accuracy
Data integration and accuracy present significant challenges in attribution modeling. Combining data from various sources can be complex and time-consuming, especially when dealing with offline and online channels. Data inconsistencies, incomplete data sets, or data fragmentation can impact the accuracy and reliability of attribution results. Ensuring the integration and accuracy of data is crucial for deriving actionable insights.
Cross-Device Tracking
As consumers use multiple devices throughout their customer journey, accurately tracking and attributing conversions across devices becomes challenging. It is essential to implement cross-device tracking techniques, such as device fingerprinting or deterministic matching, to overcome this limitation and ensure attribution models account for all touchpoints, regardless of the device used.
Offline Conversions
Attribution modeling often focuses on digital touchpoints, as online interactions are easier to track and attribute. However, for businesses that rely heavily on offline conversions, such as brick-and-mortar stores or call centers, attributing conversions to specific touchpoints becomes more challenging. Implementing solutions such as unique coupon codes, call tracking, or offline tracking mechanisms can help bridge this gap and provide a more comprehensive view of attribution.
Cannibalization and Over-attribution
Cannibalization occurs when multiple touchpoints or channels compete for credit, potentially overestimating the impact of one touchpoint over others. Over-attribution, on the other hand, can occur when a touchpoint receives more credit than it deserves, leading to inaccurate insights and resource allocation. Balancing these factors and understanding attribution model limitations is key to obtaining reliable results.
Complex Customer Journeys
The complexity of customer journeys adds another layer of challenge to attribution modeling. Customers often engage with multiple touchpoints across various channels, making it difficult to attribute a conversion to a single touchpoint accurately. The different stages, influences, and interactions involved can make it challenging to determine the exact contribution of each touchpoint, requiring a more nuanced approach to attribution modeling.
Budget Constraints
Budget constraints can limit the implementation and effectiveness of attribution modeling. Advanced attribution software and solutions often come at a cost, making them inaccessible to smaller businesses with limited resources. Allocating dedicated budgets for attribution modeling and establishing clear ROI expectations can help overcome budget constraints and justify the investment in attribution modeling.
Best Practices for Handling Attribution Modeling
Establish Clear Goals and KPIs
Clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) are fundamental to effective attribution modeling. By setting specific and measurable objectives, marketers can align their attribution strategy with their overall business goals. Identifying the KPIs that directly reflect campaign success, such as conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, or revenue generated, ensures that attribution modeling focuses on the metrics that truly matter.
Collaboration Across Marketing Teams
Attribution modeling involves multiple stakeholders across marketing teams, including digital advertising, content marketing, social media, and analytics. Collaboration and open communication among these teams are crucial for successful attribution modeling. By sharing data, insights, and feedback, teams can collectively optimize campaigns and attribution models for better results.
Regularly Review and Adjust Attribution Models
The effectiveness of attribution models can change over time as customer behavior evolves or marketing tactics shift. Regularly reviewing and adjusting attribution models enables marketers to adapt to changes and stay aligned with their objectives. By consistently evaluating the performance of attribution models and recalibrating when necessary, marketers can ensure the accuracy of their attribution insights.
Leverage Testing and Experimentation
Testing and experimentation are vital components of effective attribution modeling. By testing different attribution models on a subset of data or running A/B tests with different touchpoints, marketers can gather empirical evidence and determine the most suitable model for their unique business needs. Experimentation encourages continuous learning and improvement, helping marketers make data-driven decisions.
Employ Data-driven Decision Making
Attribution modeling is built on data, and leveraging this data for decision-making is critical. Base marketing decisions on accurate attribution insights rather than gut feelings or assumptions. Analyze data from various sources, including attribution reports, customer journey maps, and campaign analytics, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the impact of different touchpoints and channels.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The field of attribution modeling is continuously evolving, with new methodologies, technologies, and trends emerging. To stay ahead, it is essential to adopt a mindset of continuous learning and adaptation. Stay updated on industry best practices, attend conferences and webinars, and engage with industry thought leaders to stay informed about the latest advancements in attribution modeling.
Case Studies of Successful Attribution Modeling
E-commerce Industry
An e-commerce company implemented a position-based attribution model to understand the impact of their multi-channel advertising efforts. They discovered that their initial touchpoint – a blog post introducing their products – played a significant role in driving conversions. By prioritizing content creation and amplification strategies, they increased website traffic, conversions, and revenue.
B2B Marketing
A B2B marketing agency leveraged a custom attribution model that considered engagement time and industry-specific events. By attributing more credit to touchpoints with longer engagement durations and those aligned with critical industry events (such as webinars or conferences), they gained a deeper understanding of their target audience’s behavior and optimized their marketing efforts accordingly.
Mobile App Advertising
A mobile app advertising company utilized a last-touch attribution model to understand the impact of different marketing channels on app installations. They found that their influencer marketing campaigns consistently outperformed other channels in driving app downloads. By allocating more budget and resources to influencer partnerships, they significantly increased app installations and user retention.
Retail and Brick-and-Mortar Stores
A retail chain implemented a combination of offline tracking mechanisms, such as unique coupon codes and loyalty program analyses, to attribute in-store purchases to specific touchpoints. By connecting their digital marketing efforts to in-store conversions, they gained valuable insights into the effectiveness of their multi-channel campaigns, resulting in better resource allocation and increased foot traffic.
Future Trends in Attribution Modeling
Advancements in Machine Learning and AI
The integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) into attribution modeling is expected to drive significant advancements. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, identify complex patterns, and automatically adjust attribution models based on real-time optimization. Machine learning algorithms can also predict future customer behavior, enabling advertisers to proactively adjust their campaigns for better results.
Integration of Offline and Online Data
As businesses continue to operate both online and offline, integrating offline and online data will become increasingly essential. Attribution modeling will need to account for touchpoints that are not digitally trackable, such as billboards, TV advertisements, or in-store experiences. Innovations in data collection techniques, such as geolocation tracking or point-of-sale systems integration, will enable a more comprehensive view of the customer journey.
Cross-Platform and Cross-Device Attribution
With consumers using multiple devices and platforms simultaneously, tracking and attributing conversions across these channels and devices become vital. Cross-platform and cross-device attribution modeling aims to provide a holistic understanding of the customer journey, regardless of the device or platform used. Advancements in identity resolution technologies and improved user identification methods will facilitate more accurate cross-platform attribution in the future.
Privacy Regulations and Impact on Attribution
The increasing focus on user privacy and data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), will have a significant impact on attribution modeling. Stricter consent requirements and limitations on data collection and usage may impact the availability and accuracy of data for attribution. Advertisers will need to navigate these regulations while still ensuring compliance and accurate attribution insights.
Conclusion
Attribution modeling is a powerful tool in understanding the effectiveness of multi-channel advertising campaigns. By assigning credit to different touchpoints and channels, advertisers can make informed decisions about their marketing strategies, resource allocations, and optimization efforts. Understanding the various attribution models, implementing tracking and analytics systems, and analyzing attribution results are critical to successful attribution modeling. Despite the challenges and limitations, best practices, collaboration, and continuous learning can help advertisers navigate the complexities of attribution modeling and drive better campaign performance. As technology advances and consumer behavior evolves, staying adaptable and embracing emerging trends will be key to harnessing the full potential of attribution modeling in the future.